Muscle injuries are among the most common issues faced by athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and even individuals with sedentary lifestyles. From mild muscle strains to severe tears, these injuries can significantly affect mobility, strength, and overall quality of life. Fortunately, physical therapy for muscle injuries has proven to be one of the most effective ways to accelerate recovery, restore function, and prevent future problems.
In this article, we’ll explore how physical therapy works, the methods used, and why it is such a crucial component in the healing process.
Understanding Muscle Injuries
Muscle injuries occur when muscle fibers are overstretched or torn, often due to sudden force, overuse, or improper movement. They are typically categorized into three grades:
physical therapy for muscle injuries
physical therapy for muscle injuries
physical therapy for muscle injuries
-
Grade I (Mild): Small tears in the muscle fibers, causing minimal pain and swelling.
-
Grade II (Moderate): Partial tears with noticeable swelling, bruising, and loss of strength.
-
Grade III (Severe): Complete rupture of the muscle, often requiring surgery and extensive rehabilitation.
Regardless of the severity, early and appropriate treatment is essential to minimize long-term damage and speed up the return to normal activities.
How Physical Therapy Supports Healing
Physical therapy focuses on restoring the normal function of injured muscles through a combination of techniques, exercises, and modalities. A licensed physical therapist evaluates the injury and develops a personalized treatment plan to meet the patient’s specific needs.
Here are the key ways physical therapy promotes recovery:
1. Reducing Pain and Inflammation
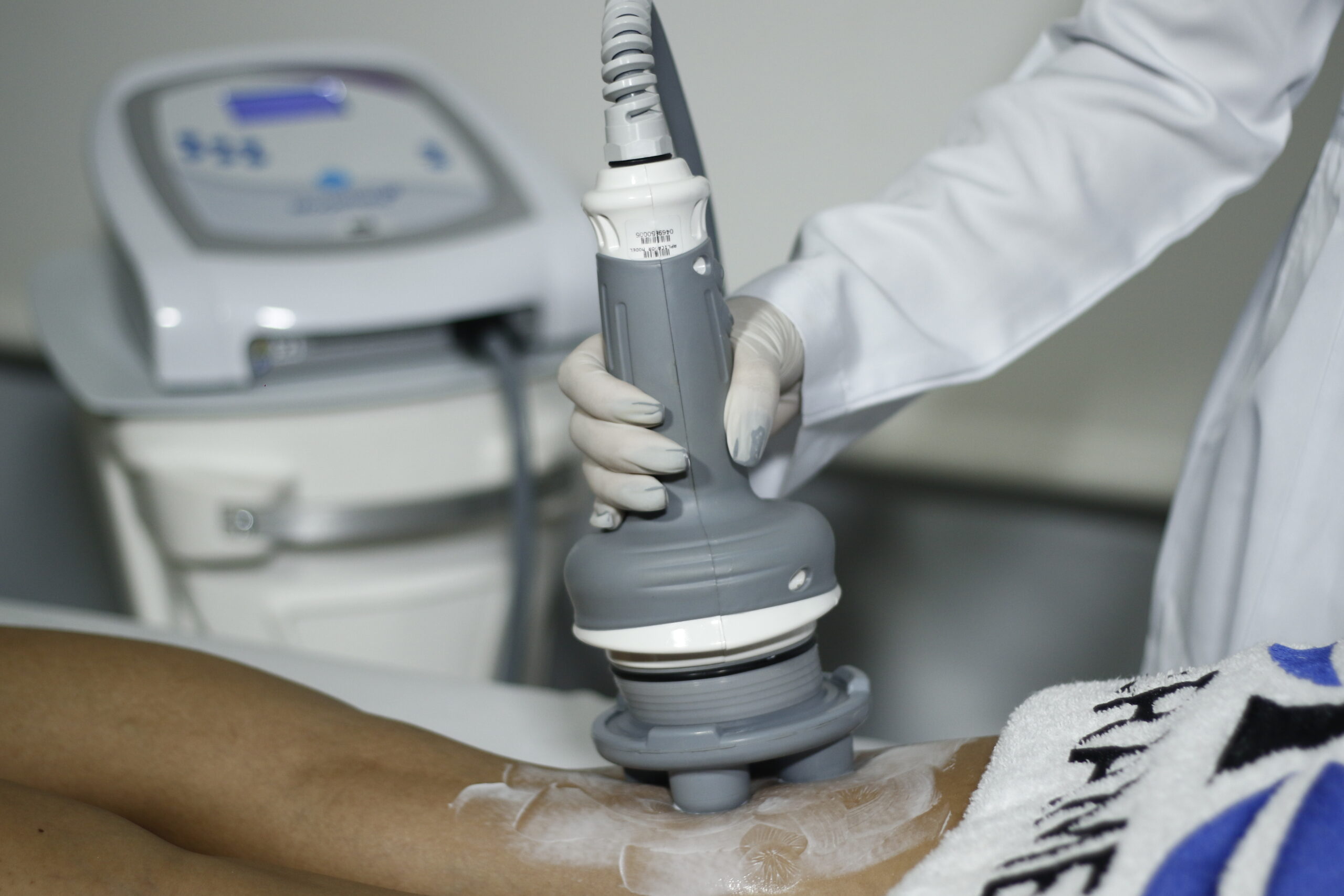
One of the first goals of physical therapy is to reduce pain and swelling. Techniques like cold therapy, compression, elevation, and gentle massage are often used in the early phase. Therapists may also use advanced technologies, such as the Modellata device from Ibramed, which uses vibro-oscillatory therapy to stimulate circulation and relieve pain without stressing the tissue.
2. Restoring Range of Motion
Muscle injuries often cause stiffness and limited mobility. Physical therapists guide patients through gentle stretching and mobility exercises to gradually restore flexibility. Regaining range of motion is essential to prevent compensatory movements that can cause new injuries.
3. Rebuilding Strength and Endurance
Once pain subsides and mobility improves, therapists introduce progressive resistance exercises to strengthen the injured muscle and surrounding areas. This not only rebuilds muscle fibers but also enhances stability, reducing the risk of reinjury.
4. Improving Blood Flow and Tissue Healing
Techniques such as manual therapy, ultrasound, and vibro-oscillatory therapy help increase blood circulation to the injured site. Better circulation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, speeding up the healing process.
5. Neuromuscular Re-education
Muscle injuries can disrupt the communication between the brain and the muscles. Physical therapists use balance training, coordination drills, and functional movement exercises to retrain the neuromuscular system, ensuring proper muscle activation during everyday movements.
Preventing Future Injuries
Another major benefit of physical therapy is its preventive approach. Therapists educate patients on proper posture, movement mechanics, warm-up routines, and strengthening exercises that lower the risk of future injuries. This proactive strategy is especially valuable for athletes or individuals returning to high levels of physical activity.
The Role of Advanced Therapies
Modern rehabilitation often combines traditional physical therapy with advanced tools. For example, the Modellata device delivers controlled oscillatory vibrations that stimulate muscles, improve circulation, and accelerate tissue repair. Incorporating such technologies can significantly shorten recovery time and improve treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
Physical therapy for muscle injuries is not just about recovery — it’s about restoring full function, preventing complications, and empowering patients to move confidently again. Through personalized care, evidence-based techniques, and innovative tools like the Modellata, physical therapy offers a safe and effective pathway back to strength and mobility.
If you or someone you know is dealing with a muscle injury, seeking professional physical therapy can make all the difference between a slow, incomplete recovery and a strong, lasting one.